Reducing heat loss in a vacuum flask involves minimizing the transfer of heat through conduction, convection, and radiation. A vacuum flask, also known as a thermos, is designed to keep the contents hot or cold for extended periods by creating a vacuum between two layers of material. Here's how you can further enhance its heat retention properties:
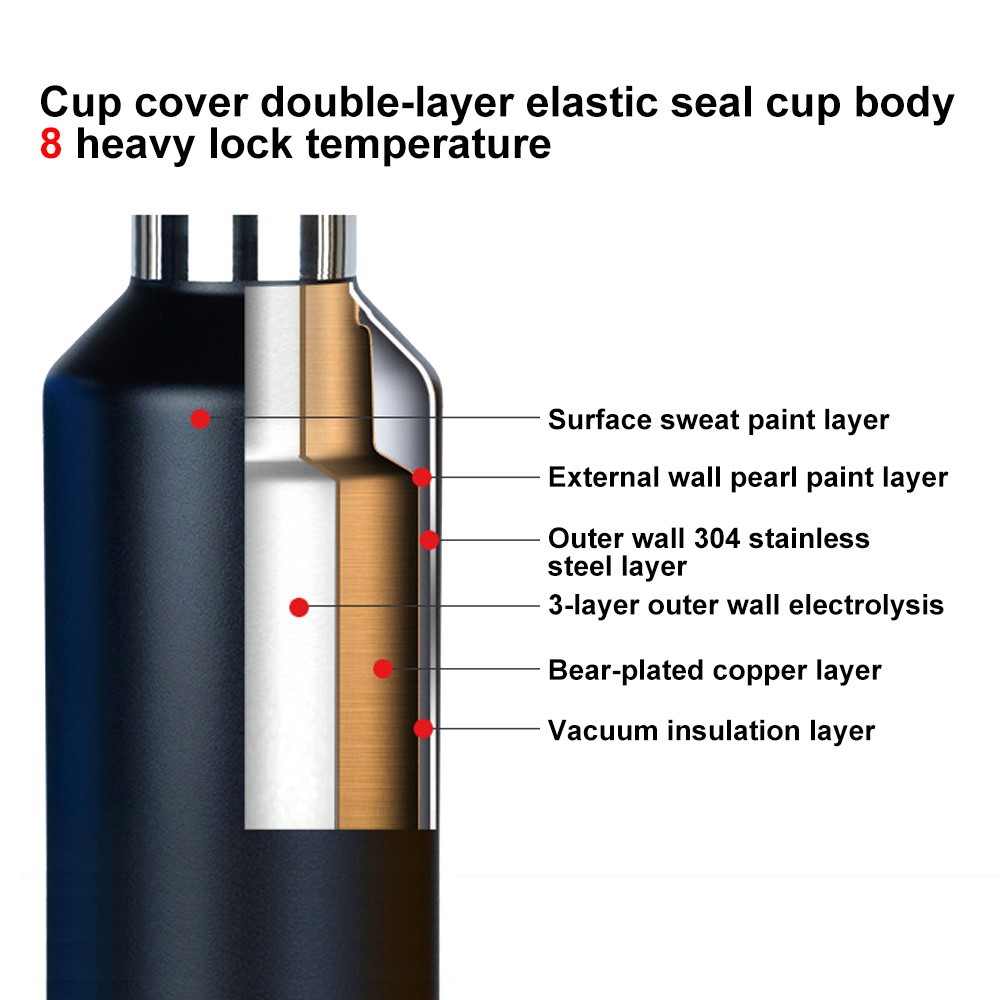
Double-Walled Construction: Vacuum flasks consist of two layers of materials with a vacuum in between. The inner layer holds the liquid, and the outer layer provides insulation. Make sure the flask has a proper double-walled construction to ensure efficient heat retention.
High-Quality Insulation: The insulating material between the walls of the flask should be of high quality and have low thermal conductivity. Common insulating materials include foam, rubber, or other synthetic materials. Higher-quality flasks often use superior insulating materials.
Reflective Coatings: Some vacuum flasks have a reflective coating on the inner surface of the outer wall. This coating helps to reduce heat transfer through radiation, as it reflects thermal radiation back into the flask.
Tight-Fitting Stopper or Lid: The stopper or lid of the vacuum flask should fit tightly to prevent air from entering or escaping. Air can carry heat through convection, so a good seal is essential.
Low-Conduction Materials: The materials used in the flask should have low thermal conductivity. Stainless steel is a common choice for the outer shell due to its insulating properties. The inner container might also be made of stainless steel or glass, which are both low-conduction materials.
Evacuated Space Maintenance: Over time, the vacuum between the walls of the flask can degrade due to various reasons, including temperature changes and manufacturing defects. Make sure your flask is well-made and doesn't develop leaks or breaks in the vacuum layer.
Minimize Opening: Opening the flask frequently allows heat exchange with the surroundings. Minimize opening the flask as much as possible to retain the temperature.
Preheat or Precool: Before filling the flask with the desired liquid, preheat (for hot liquids) or precool (for cold liquids) the flask by adding hot water or ice water, respectively. This helps the flask maintain the desired temperature more effectively.
Protect from Extreme Temperatures: Vacuum flasks are designed to work optimally within a certain temperature range. Exposing the flask to extreme heat or cold can impact its performance.
Choose a Quality Flask: Investing in a high-quality vacuum flask from a reputable brand can ensure better insulation and heat retention. Look for flasks with good reviews and features that emphasize heat retention.
By following these tips, you can maximize the heat retention capabilities of your vacuum flask and keep your liquids hot or cold for longer periods.